Case Identification
Case ID Number
Tumor Type
Body region
Position within the bone
Periosteal reaction
Benign or Malignant
Clinical case information
Case presentation
The patient is a 44-year-old machinist who has had pain in the right hip for approximately one year. It is exacerbated by standing, walking and heavy activity, and somewhat relieved by rest.
Radiological findings:
There is no significant night pain but there may be a dull ache. Motrin does not relieve the pain. There is no significant past history or family history.
On examination of the right hip there is an excellent full range of motion without apparent pain. There is some anterior irritability to deep palpation but no mass can be appreciated. There is no skin abnormality, no ecchymosis, no warmth. No other pertinent findings are noted on the exam.
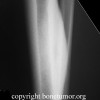
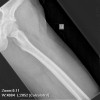
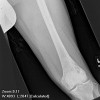
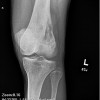
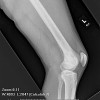
Plain radiographs, CT scan, bone scan are available for review. There is a mixed lytic and sclerotic lesion in the proximal femur, centrally located in the intramedullary space, just above the lesser trochanter. The cortex does not appear to be violated. The area in the center of the lesion is lucent without matrix. Surrounding this is a very dense area of sclerosis which is somewhat irregular.
The CT scan shows essentially similar findings but shows that the lesion is larger when seen on CT that when seen on radiographs. The central area is actually two lobulated central lucent defects in the bone. The lesion is very slightly increased uptake on bone scan. No other areas of abnormality on the bone scan are appreciated.
On examination of the right hip there is an excellent full range of motion without apparent pain. There is some anterior irritability to deep palpation but no mass can be appreciated. There is no skin abnormality, no ecchymosis, no warmth. No other pertinent findings are noted on the exam.
Plain radiographs, CT scan, bone scan are available for review. There is a mixed lytic and sclerotic lesion in the proximal femur, centrally located in the intramedullary space, just above the lesser trochanter. The cortex does not appear to be violated. The area in the center of the lesion is lucent without matrix. Surrounding this is a very dense area of sclerosis which is somewhat irregular.
The CT scan shows essentially similar findings but shows that the lesion is larger when seen on CT that when seen on radiographs. The central area is actually two lobulated central lucent defects in the bone. The lesion is very slightly increased uptake on bone scan. No other areas of abnormality on the bone scan are appreciated.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this lesion should include fibrous dysplasia, fibroxanthoma (non-ossifying fibroma), polymorphic fibro-osseous tumor of bone, liposclerosing myxofibrous tumor of bone, myxofibroma, lipoma, cyst, bone infarct, Paget's disease, and, chondroma. The lesion is too large for an osteoid osteoma but might be an osteoblastoma. The lesion does not have aggressive features so osteosarcoma is unlikely. No orthopedic surgeon considering a bone-forming lesion in the femur should fail to at least consider osteosarcoma, regardless of the age of the patient.
Special Features of this Case:
The tumor is a polymorphic fibro-osseous tumor of bone, also called a liposclerosing myxofibrous tumor of bone. On pathology, the lesion is composed of crudely woven bone that may have a pagetoid appearance. surrounded by fibrous tissue. Fat and myxoid change may also be present. The lesion may mimic fibrous dysplasia.
This tumor is usually in the proximal femur.. A diagnosis must be based on the combination of the location and appearance with the predominant histological pattern. These lesions are usually incidental findings. The age range is broad, usually adults, The tumors probably arise in childhood. Their appearance may evolve slowly over time.
The tumor may not have features that allow diagnosis without careful biopsy, thus observation only is not appropriate management of this tumor. After biosy, this tumor does not require aggressive resection. Treatment by curettage is sufficient. The patient should be followed to check for progression. In parallel with some enchondromas and bone infarcts, a minority of lesions undergo malignant transformation.
References:
Hum Pathol. 1993 May; 24(5): 505-12.
Polymorphic fibro-osseous lesions of bone: an almost site-specific diagnostic problem of the proximal femur.
Ragsdale BD.
This lesion was biopsied by minimally invasive means, with an approach calculated to minimize the risk of biopsy-induced pathologic fracture as well as to minimize the risk of contamination of uninvolved structures which might complicate limb salvage if it became necessary. The tumor is a polymorphic fibro-osseous tumor of bone, also called a liposclerosing myxofibrous tumor of bone. This tumor does not require aggressive resection. Treatment by curettage is sufficient. In in this case the patient will be followed to check for progression.
This tumor is usually in the proximal femur.. A diagnosis must be based on the combination of the location and appearance with the predominant histological pattern. These lesions are usually incidental findings. The age range is broad, usually adults, The tumors probably arise in childhood. Their appearance may evolve slowly over time.
The tumor may not have features that allow diagnosis without careful biopsy, thus observation only is not appropriate management of this tumor. After biosy, this tumor does not require aggressive resection. Treatment by curettage is sufficient. The patient should be followed to check for progression. In parallel with some enchondromas and bone infarcts, a minority of lesions undergo malignant transformation.
References:
Hum Pathol. 1993 May; 24(5): 505-12.
Polymorphic fibro-osseous lesions of bone: an almost site-specific diagnostic problem of the proximal femur.
Ragsdale BD.
This lesion was biopsied by minimally invasive means, with an approach calculated to minimize the risk of biopsy-induced pathologic fracture as well as to minimize the risk of contamination of uninvolved structures which might complicate limb salvage if it became necessary. The tumor is a polymorphic fibro-osseous tumor of bone, also called a liposclerosing myxofibrous tumor of bone. This tumor does not require aggressive resection. Treatment by curettage is sufficient. In in this case the patient will be followed to check for progression.
Image

Case ID Number
Image Types
Image modality
Tumor Name
Tumor Type
Benign or Malignant
Body region
Bone name
Location in the bone
periosteal reaction
position within the bone
Tumor behavior
Tumor density