Tumor List
| Case | Symptoms and Presentation |
|---|---|
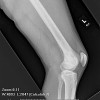
| Osteosarcoma - conventional | The most common presentation is pain and a mass, which occurs near a joint. The pain may initially accompany activity, at gradually becomes more constant and may be severe at night. Patient otherwise may have few were no symptom. |
| High-Grade surface osteosarcoma | |
| Small cell osteosarcoma | Similar to those of conventional osteosarcoma. |
| Periosteal osteosarcoma | Patient present with local pain and a mass, that may be on the diaphysis and anterior cortex of the bone, especially when the tumor involved the tibia. |
| Paget's Disease | Paget's sarcoma usually presents as a new, progressive pain in a patient with long standing Paget's disease. Other symptoms can include soft tissue swelling or pathological fractures. The serum alkaline phosphatase which is elevated with Paget's disease may rise further with onset of sarcoma. |
| Parosteal osteosarcoma | The tumor presents with a slow growing mass and mild pain. Occasionally, patients have no pain whatsoever. The most common locations are the distal femur near the back of the knee and the proximal humerus near the shoulder. |
| Periosteal chondroma | Symptoms are present for 1 to 5 years. Patients complain of a tender swelling or mass. |
| Periosteal chondroma - Foot and Ankle | The lesion presents with pain and swelling. |
| Periosteal osteosarcoma | Patient present with local pain and a mass, that may be on the diaphysis and anterior cortex of the bone, especially when the tumor involved the tibia. |
| Florid reactive periostitis | Examination reveals a tender mass with mild surrounding warmth and erythema, but no fever or adenopathy. Laboratory studies typically show a normal white blood-cell count and differential and a mildly elevated sedementation rate. Electrolytes and other laboratory values are unaffected. Plain radiographs show the tumor is adjacent to the bone rather than arising from it. Soft tissue swelling is seen as well as a marked periosteal reaction. There may be new bone formation in the soft tissues and subtle cortical thinning. In rare cases there is local erosion of the cortex. Technetium-99 bone scans show a solitary focus of intense uptake. Magnetic resonance scans show a mass and striking signal abnormalities in the soft tissues as well as the nearby bone marrow that are relatively nonspecific and are consistent with infection, trauma, or tumor. |
| Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis | It presents as a painless or mildly painful joint with swelling. |
| Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis - Foot and Ankle | The lesion most commonly presents as a localized, nodular mass in or adjacent to a joint or tendon sheath. The nodular form occurs around the joints and tendons of the hands and feet. The diffuse form usually involves larger joints, and may involve several adjacent joints. |
| Plantar fibroma - Foot and Ankle | Most patients are asymptomatic, but some have activity related pain. One third to half of the patients have bilateral nodules. Pain occurs with weightbearing activities. When the lesions are large enough to press on the plantar nerves, there may be numbness or dysesthesia in the distal portions of the foot. In one pediatric patient, a large lesion caused contracture of the toe flexor tendons and loss toe extension in the lesser toes. |
| Polimórfica Fibroóseo Lesión del Hueso | Este tumor se presenta con dolor. |
| Post - Paget’s Sarcoma | Paget's sarcoma usually presents as a new, progressive pain in a patient with long standing Paget's disease. Other symptoms can include soft tissue swelling or pathological fractures. The serum alkaline phosphatase which is elevated with Paget's disease may rise further with onset of sarcoma. |
| Post - Paget’s Sarcoma | Paget's sarcoma usually presents as a new, progressive pain in a patient with long standing Paget's disease. Other symptoms can include soft tissue swelling or pathological fractures. The serum alkaline phosphatase which is elevated with Paget's disease may rise further with onset of sarcoma. |
| Post radiation osteosarcoma - post radiation sarcoma | Symptoms can go unnoticed for a fairly long time, or be misinterpreted by the patient and the doctor, and then an acute onset of constant and progressive pain and/or swelling occurs. The pain is worse at night and is usually not relieved with aspirin or nonsteroidal drugs. Other symptoms include a development of a mass and/or a pathologic fracture near to the irradiation area with tenderness and/or bleeding. |
| runner's bump - Foot and Ankle | The mass typically presents after a minor change in the training program or an insignificant injury. The lesion increases in size with running and activities and decreases in size with rest and elevation. Pain is usually mild enough to allow continuation of the running program, which in turn leads to the persistence of the lesion. |
| Aneurysmal Bone Cyst | Gradually increasing pain, a mass, or with a pathological fracture through the lesion. Rapid increase is lesion size has been reported in a few cases. |
| Unicameral Bone Cyst | Most UBC's are asymptomatic and only present when a pathological fracture occurs. |