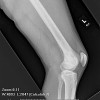
Tumor List
| Case | Symptoms and Presentation |
|---|---|
| Hemangioendothelioma | |
| Hemangioendothelioma | |
| Hemangioma | Hemangiomas are usually asymptomatic lesions discovered on x-ray or autopsy. Vertebral hemangiomas can cause neurological symptoms if they extend into the epidural space. Symptoms may vary with other factors that cause vascular distension or reactivity, such as dependency, activity, pregnancy and menstruation. |
| Epithelioid Hemangioma | Clinically, patients usually present with pain over the involved sites. |
| Hemangiopericytoma | Clinically, hemangiopericytomas may present with pain or a mass. The lesions grow slowly so it may be twenty years before a diagnosis is made. |
| Hemangiopericytoma | Clinically, hemangiopericytomas may present with pain or a mass. The lesions grow slowly so it may be twenty years before a diagnosis is made. |
| Hibernoma | This tumor is typically asymptomatic and presents as a fleshy painless mass, with size at presentation ranging from 1 to 24 cm, with an average size of 9.3 cm. The tumor may be present from one month to 10 years, or may be an incidental finding. |
| High-Grade surface osteosarcoma | |
| Benign Fibrous Histiocytoma | Clinically, patients report pain from the lesion, often of months or years duration. Pain may be associated with pathological fracture. There may be some local tenderness, but no swelling or mass is seen, and there are no systemic symptoms. There is normally no impairment of the function of the nearby joint. Spinal lesions may cause neurologic defect by pressing on the spinal cord. In some cases there is a primary underlying disorder of cholesterol metabolism or other lipid abnormalities. In these cases the lytic bone lesions are analogous to those seen in storage diseases such as Gaucher's disease. These multiple lesions are termed "xanthoma disseminatum". One reported case is of a 10 year old boy with lytic lesions in the pelvis, femur, and humerus, as well as yellow and brown papules and plaques on the face and trunk. This patient also had polyuria and polydipsia, and was found to have diabetes insipidus. (Khandpur) Radiographically, the lesion occur commonly in the ribs, pelvis, including the sacrum and ilium, or in the epiphysis or diaphysis of tubular bones. These tumors have been reported in the jaw and associated soft tissues. In another report this tumor occurred commonly around the knee. |
| Malignant fibrous histiocytoma | Clinically, MFH presents with local pain and swelling. There is often a history of a rapidly enlarging mass. Pathologic fractures are present 20% of the time. Radiologically, MFH is an aggressive, permeative lesion which often lacks distinctive features found in other high grade primary bone malignancies. It usually presents with a soft tissue mass with or without cortical erosion. There is not normally a periosteal reaction. |
| Hodgkin's Lymphoma of the Bone | Usually pain is the presenting symptom in primary bone disease. Weight loss and malaise may be absent. Lytic lesions are most common, but mixed or sclerotic lesions can also be seen. Lesions may be associated with a periosteal reaction. Bone scintigraphy is useful in detection of skeletal HD. MRI is very sensitive in the localization of subtle marrow disease. Marrow involvement produces a hypointense signal on T1 weighted spin echo sequences and high signal on T2 weighted gradient echo sequences. |
| Bone island | |
| Intraosseous Well-differentiated Osteosarcoma | Low-grade Osteosarcoma's often present themselves as pathologic fractures. |
| Intraosseous venous drainage anomaly | |
| Intraosseous Well-differentiated Osteosarcoma | Low-grade Osteosarcoma's often present themselves as pathologic fractures. |
| Jaffe-Campanacci Syndrome | The skin lesions are cafe au lait patches, which are brown to dark brown and usually found on the trunk. Not all patients with this syndrome have skin patches. Most of the patches had a smooth border. Cafe au lait patches with complex border can also be found. The cutaneous features of neurofibromatosis (NF), such as angiomas and neurofibromas, may also be present. There may be axillary freckling. Recent findings suggest that JCS may be a form of NF. Patients with suspected JCS should be screened for NF. |
| Juxtacortical chondroma | Mild pain or symptoms arising from the nearby joint. |
| Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis (CRMO) | Children present with pain, deep aching pain, limping, and may also present with fever. The metaphyseal area of long bones, the clavicle, and the shoulder girdle are common locations. Other sites such as the spine, ankle, and foot have been reported. Dermatological manifestations may occur and include psoriasis, acne, and pustules on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. Uveitis, and inflammatory bowel disease have also been described. Majeed syndrome consists of CRMO and congenital dyserythropoietic aneama, has been reported in families. Te LPIN2 gene appears to play a role in these cases. |
| Leiomyoma of deep soft tissue | A slow growing, minimally painful mass in the deep subcutaneous tissues of the extremities. |
| Leiomyosarcoma - Bone and Soft Tissue |